DTC P2B61:00 [PCM (SKYACTIV-G (US))]
DTC P2B61:00 [PCM (SKYACTIV-G (US))]
SM2565530
id0102t41680u0
-
Note
-
• To determine the malfunctioning part, proceed with the diagnostics from “Function Inspection Using M-MDS”.
Details On DTCs
|
Description |
Coolant control valve circuit range/performance |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Detection condition
|
Determination conditions
|
• The coolant control valve control duty value is 89% or more for a continuous 2 s.
|
|
|
Preconditions
|
• Not applicable
|
||
|
Drive cycle
|
• 1
|
||
|
Self test type
|
• CMDTC self test
|
||
|
Sensor used
|
• Coolant control valve position sensor
|
||
|
Fail-safe function
|
• PCM restricts engine torque.
|
||
|
Vehicle status when DTCs are output
|
• Not applicable
|
||
|
Possible cause
|
• Coolant control valve connector or terminals malfunction
• PCM connector or terminals malfunction
• Coolant control valve sticking, or foreign matter penetration
• Short to ground in coolant control valve control circuit
• Short to ground in any of the following coolant control valve position sensor circuits.
• Short circuit in coolant control valve control circuits
• Short circuit between any of the following coolant control valve position sensor circuits.
• Open circuit in coolant control valve control circuit
• Open circuit in any of the following coolant control valve position sensor circuits.
• Coolant control valve malfunction
• Coolant control valve position sensor malfunction
• PCM malfunction
|
||
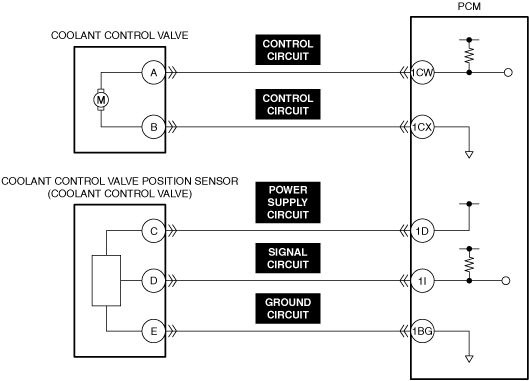 |
|||
 |
|||
 |
|||
Function Explanation (DTC Detection Outline)
Repeatability Verification Procedure
1.Warm up the engine to allow the engine coolant temperature to reach 50—95 °C {122—203 °F}.
-
Note
-
• The difference between PIDs ENG_COOL_VLV_POS_ACT and ENG_COOL_VLV_POS_COMD displayed the engine coolant control valve opening angle must be within 2 °.• Match the engine coolant temperature in the recorded freeze frame data/snapshot data, the vehicle speed, and engine speed values to the best extent possible while driving the vehicle.
2.Try to reproduce the malfunction by driving the vehicle for 5 min based on the values in the freeze frame data/snapshot data.
PID Item/Simulation Item Used In Diagnosis
PID/DATA monitor item table
|
PIDs |
Reference |
|---|---|
|
ENG_COOL_VLV_POS_COMD
|
|
|
ENG_COOL_VLV_POS_ACT
|
Function Inspection Using M-MDS
|
Step |
Inspection |
Results |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
PURPOSE: IDENTIFY TRIGGER DTC FOR FREEZE FRAME DATA
• Is the DTC P2B61:00 on freeze frame data?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Go to the troubleshooting procedure for DTC on freeze frame data.
|
||
|
2
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY RELATED REPAIR INFORMATION OR SERVICE INFORMATION AVAILABILITY
• Verify related Service Bulletins, on-line repair information, or Service Information availability.
• Is any related Information available?
|
Yes
|
Perform repair or diagnosis according to the available information.
• If the vehicle is not repaired, go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
3
|
PURPOSE: RECORD VEHICLE STATUS WHEN DTC WAS DETECTED TO UTILIZE WITH REPEATABILITY VERIFICATION
• Record the freeze frame data/snapshot data.
|
—
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
4
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT FOR OTHER RELATED DTCs
• Perform the DTC inspection for the PCM. (See DTC INSPECTION.)
• Are any other DTCs displayed?
|
Yes
|
Repair the malfunctioning location according to the applicable DTC troubleshooting.
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
5
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY COOLANT CONTROL VALVE POSITION SENSOR INPUT SIGNAL
• Start the engine and idle it.
• Access the ENG_COOL_VLV_POS_ACT PID using the M-MDS. (See PID/DATA MONITOR INSPECTION.)
• Is the PID value within specification?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Go to Troubleshooting Diagnostic Procedure to perform the procedure from Step 1.
|
||
|
6
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY CONNECTOR CONNECTIONS
• Start the engine.
• Access the ENG_COOL_VLV_POS_ACT PID using the M-MDS. (See PID/DATA MONITOR INSPECTION.)
• Does the PID value fluctuate when the following connectors are shaken?
|
Yes
|
Inspect the related wiring harness and connector.
• Repair or replace the malfunctioning part.
Go to Troubleshooting Diagnostic Procedure to perform the repair completion verification.
|
|
No
|
Go to Troubleshooting Diagnostic Procedure to perform the procedure from Step 1.
|
Troubleshooting Diagnostic Procedure
-
― Perform an inspection of the connectors and wiring harnesses between the coolant control valve and the PCM.
-
― Perform a unit inspection of the coolant control valve.
-
― Perform a unit inspection of the coolant control valve position sensor.
-
― Verify that the primary malfunction is resolved and there are no other malfunctions.
|
Step |
Inspection |
Results |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY IF COOLANT CONTROL VALVE IS INSTALLED CORRECTLY
• Verify the coolant control valve installation condition. (See COOLANT CONTROL VALVE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION [SKYACTIV-G (WITH CYLINDER DEACTIVATION (US))].) (See COOLANT CONTROL VALVE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION [SKYACTIV-G (WITHOUT CYLINDER DEACTIVATION (US))].)
• Is the installation condition normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Correctly install the coolant control valve and perform the repair completion verification.
|
||
|
2
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT COOLANT CONTROL VALVE CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND
• Inspect the applicable circuit for a short to ground. (See CIRCUIT INSPECTION.)
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification.
|
||
|
3
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT COOLANT CONTROL VALVE POSITION SENSOR POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS, SIGNAL CIRCUITS, AND GROUND CIRCUITS FOR SHORT TO GROUND
• Inspect the applicable circuit for open circuit. (See CIRCUIT INSPECTION.)
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification.
|
||
|
4
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT COOLANT CONTROL VALVE CONTROL CIRCUITS FOR SHORT CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuits for a short circuit. (See CIRCUIT INSPECTION.)
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification.
|
||
|
5
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT COOLANT CONTROL VALVE POSITION SENSOR POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS, SIGNAL CIRCUITS, AND GROUND CIRCUITS FOR SHORT CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuits for a short circuit. (See CIRCUIT INSPECTION.)
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification.
|
||
|
6
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT COOLANT CONTROL VALVE CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuit for open circuit. (See CIRCUIT INSPECTION.)
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification.
|
||
|
7
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT COOLANT CONTROL VALVE POSITION SENSOR POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS, SIGNAL CIRCUITS, AND GROUND CIRCUITS FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
• Inspect the applicable circuit for open circuit. (See CIRCUIT INSPECTION.)
• Is the circuit normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification.
|
||
|
8
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT COOLANT CONTROL VALVE FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part. (See COOLANT CONTROL VALVE INSPECTION [SKYACTIV-G (WITH CYLINDER DEACTIVATION (US))].) (See COOLANT CONTROL VALVE INSPECTION [SKYACTIV-G (WITHOUT CYLINDER DEACTIVATION (US))].)
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification.
|
||
|
9
|
PURPOSE: INSPECT COOLANT CONTROL VALVE POSITION SENSOR FOR MALFUNCTION
• Inspect the applicable part. (See COOLANT CONTROL VALVE POSITION SENSOR INSPECTION [SKYACTIV-G (WITH CYLINDER DEACTIVATION (US))].) (See COOLANT CONTROL VALVE POSITION SENSOR INSPECTION [SKYACTIV-G (WITHOUT CYLINDER DEACTIVATION (US))].)
• Is the part normal?
|
Yes
|
Go to the next step.
|
|
No
|
Repair or replace the malfunctioning location and perform the repair completion verification.
|
||
|
Repair completion verification 1
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY THAT VEHICLE IS REPAIRED
• Install/connect the part removed/disconnected during the troubleshooting procedure.
• Clear the DTC recorded in the memory. (See CLEARING DTC.)
• Replicate the vehicle conditions at the time the DTC was detected using the following procedure.
• Perform the DTC inspection for the PCM. (See DTC INSPECTION.)
• Is the same Pending DTC present?
|
Yes
|
Refer to the controller area network (CAN) malfunction diagnosis flow to inspect for a CAN communication error.
If the CAN communication is normal, perform the diagnosis from Step 1.
• If the malfunction recurs, replace the PCM, then go to the next step. (See PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION [SKYACTIV-G (WITH CYLINDER DEACTIVATION (US))].) (See PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION [SKYACTIV-G (WITHOUT CYLINDER DEACTIVATION (US))].)
|
|
No
|
Go to the next step.
|
||
|
Repair completion verification 2
|
PURPOSE: VERIFY IF OTHER DTCs DISPLAYED
• Perform the DTC inspection. (See DTC INSPECTION.)
• Are any other DTCs displayed?
|
Yes
|
Repair the malfunctioning location according to the applicable DTC troubleshooting.
|
|
No
|
DTC troubleshooting completed.
|