ELECTRONIC SPARK ADVANCE CONTROL [SKYACTIV-G (WITHOUT CYLINDER DEACTIVATION (US))]
ELECTRONIC SPARK ADVANCE CONTROL [SKYACTIV-G (WITHOUT CYLINDER DEACTIVATION (US))]
SM2565333
id0140u0188200
Outline
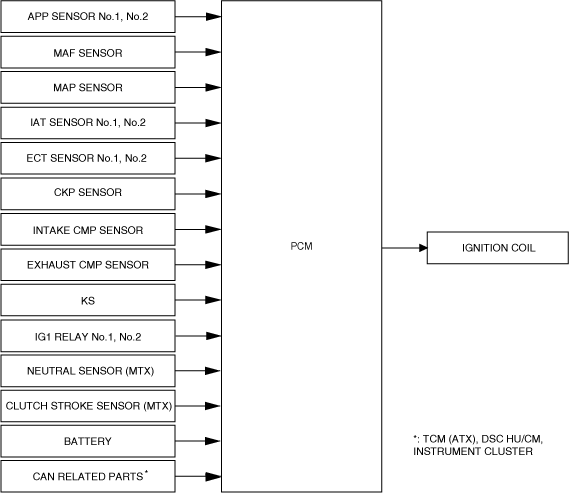
Block Diagram
am3zzn00008276
|
Operation
Ignition method
-
• The PCM energizes the ignition coils according to the ignition timing calculated from the engine operation conditions and the igniter energization time.• The igniter energization time (ignition coil energization time) is determined according to battery voltage and engine speed.
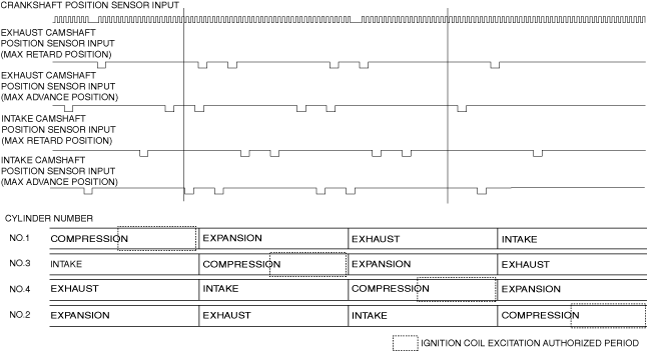
Timing chart
am3zzn00003421
|
Determination of Ignition Timing
-
Division of control zones
-
• The PCM performs different ignition controls for engine starting and those other than engine starting to stabilize the engine starting.
|
Control zone |
Control condition |
Ignition method |
|---|---|---|
|
Engine start zone
|
Engine speed is less than 500 rpm
|
Engine starting
|
|
Normal zone
|
Engine operation except start zone
|
(Cycle estimated ignition) (Determines ignition timing adding each correction to basic spark advance)
|
Ignition timing calculation method table
A: Ignition timing base, B: Correction for ignition timing
|
Contents
|
Calculation method or determination method for ignition timing, spark advance, and correction
|
Control zone
|
||
 |
 |
|||
|
Starting ignition
|
Determination based on engine coolant temperature
|
A
|
||
|
Cycle estimated ignition
|
Basic spark advance
|
Set value according to engine speed and charging efficiency*
|
A
|
|
|
Correction
|
Engine coolant temperature spark advance correction
|
Purpose: Ensures combustion stability when engine coolant temperature is low
According to engine coolant temperature
• High charging efficiency *, low engine coolant temperature→large correction
|
B
|
|
|
Intake air temperature correction
|
Purpose: Suppresses knocking when engine intake air temperature is high
According to engine intake air temperature and engine coolant temperature
• High engine intake air temperature, high engine intake air temperature→large correction
|
B
|
||
|
Warm-up promotion spark retard correction
|
Purpose: Activates the catalytic converter earlier
Maximum 50 s after engine start
• According to engine coolant temperature→correction
|
B
|
||
|
Torque reduction correction
|
Purpose: Such as reduction of shift shock, traction control, or suppression of vehicle vibration
According to torque reduction request from TCM, or DSC
• Large torque reduction request→large correction
|
B
|
||
|
Knocking spark retard correction
|
Purpose: Knocking suppression
Acceleration when charging efficiency * volume increase (acceleration amount) is given value or more
• Large acceleration amount→large correction
|
B
|
||
|
Valve timing correction
|
Purpose: Ensures combustion stability
When phase difference changes due to electric variable valve timing control and variable valve timing control
• Correction according to change in phase difference
|
B
|
||
-
• If immobilizer system related information (engine start prohibited) is received from the BCM, the PCM stops ignition.• When a collision signal is received from the SAS control module, the PCM stops the ignition.