DYNAMIC STABILITY CONTROL (DSC) [(US)]
DYNAMIC STABILITY CONTROL (DSC) [(US)]
SM2334033
id0415001046x1
Outline
DSC operation outline
-
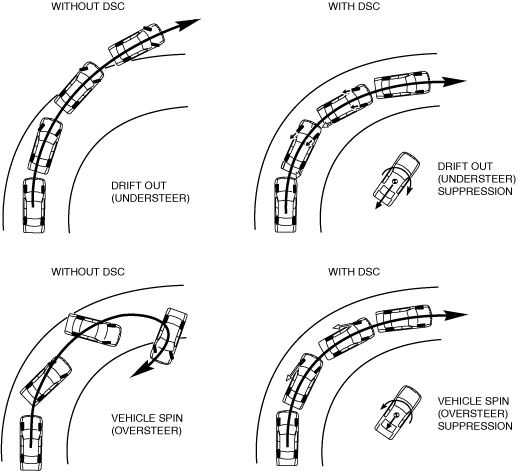
• The ABS prevents wheel lock-up during braking. The TCS detects drive wheel spin due to the accelerator pedal being pressed too hard or similar causes and controls engine speed to suppress wheel spin. With these systems, safety is assured when driving or stopping.• Additionally, sudden changes in vehicle attitude, due to evasive steering or road conditions, are controlled by the DSC. The DSC suppresses vehicle sideslip when driving due to vehicle spin (oversteer) or drift-out (understeer) by controlling braking and engine speed. At this time, the TCS/DSC indicator light illuminates to alert the driver that the DSC is operating due to a dangerous situation. As a result, the driver can calmly react and is provided leeway for the next maneuver, resulting in safe driving conditions.• In this way the combination of DSC + ABS + TCS ensures driving, stopping and turning safety in all aspects.
Results of DSC operation
ac5wzn00000240
|
-
Caution
-
• While the DSC is a steering safety system, it does not improve normal steering function. Therefore, always drive carefully, even if the vehicle has DSC, and do not overestimate the DSC capability.• If the initialization procedures for the brake fluid pressure, low-G, and yaw rate sensors are not performed correctly, an incorrectly determined initial point may cause a discrepancy between the actual driving conditions of the vehicle and the signals from the sensors, resulting in improper DSC operation. Therefore, after replacing the following parts, make sure to perform the DSC HU/CM initialization procedures of the sensors with the vehicle stopped on a level ground to insure proper DSC operation. For the initialization procedures of the sensors, refer to the Workshop Manual.
-
― DSC HU/CM― SAS control module
• The DSC and ABS will not operate normally under the following conditions:-
― With tires that are not of the specified size, manufacturer or tread pattern, or not inflated according to specification― With tires that have significant comparative wear variation― With tire chains― With an emergency spare tire
-
Structural View
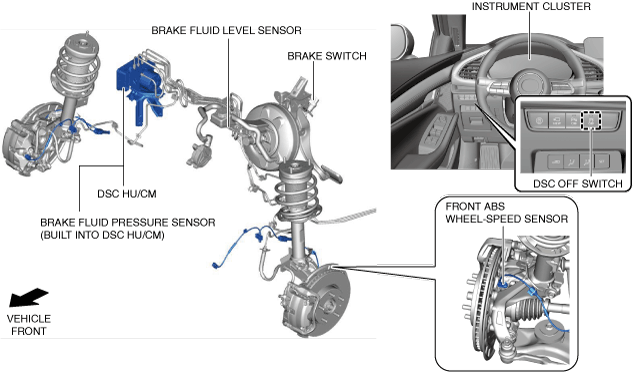
Vehicle front side
am3zzn00009805
|
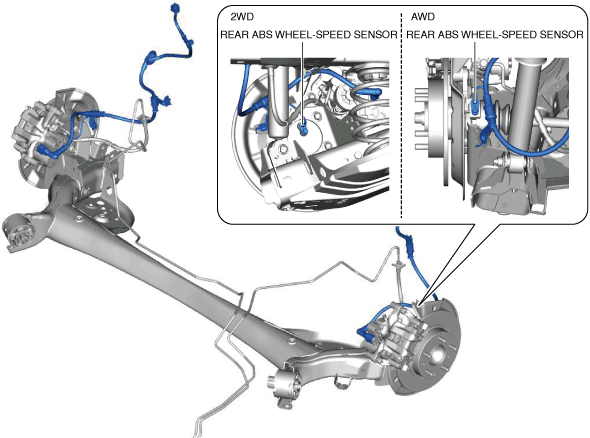
Vehicle rear side
am3zzn00009754
|
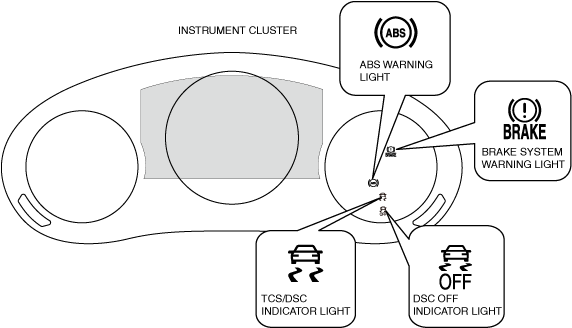
Warning light and indicator light
am3zzn00007921
|
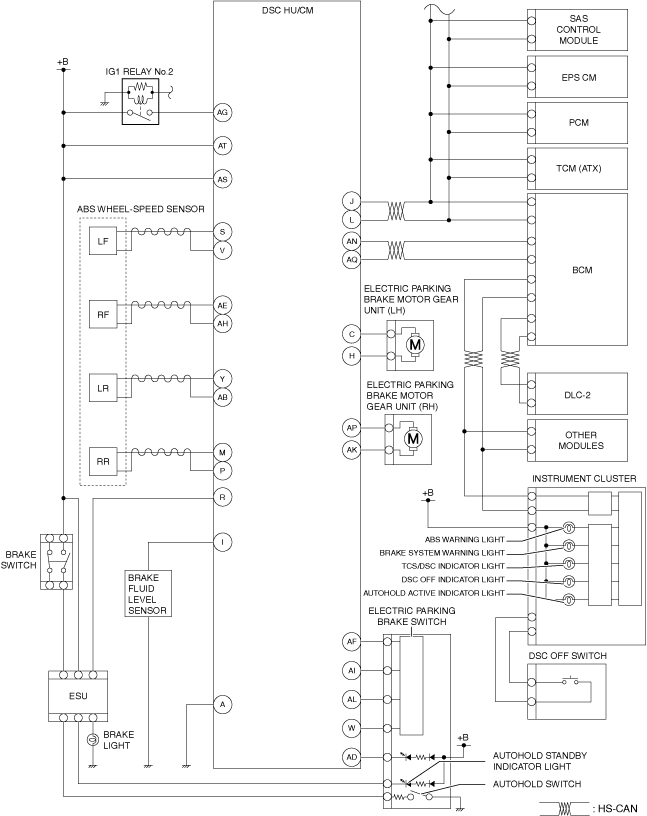
System Wiring Diagram
am3zzn00009755
|
Construction
|
Part name |
Function |
|---|---|
|
DSC HU/CM
|
• Makes calculations using input signals from each sensor, controls brake fluid pressure to each wheel, and actuates function (ABS, EBD, TCS, DSC, brake assist control, Hill Launch Assist (HLA), and Secondary Collision Reduction *) of the DSC system.
• Outputs the torque reduction request signal, wheel speed signal, and DSC system warning control data via CAN lines.
• Controls the on-board diagnostic system and fail-safe function when there is a malfunction in the DSC system.
|
|
PCM
|
• Controls engine output based on signals from the DSC HU/CM.
• Transmits engine speed, engine torque, brake switch status, and accelerator pedal position data via CAN communication to the DSC HU/CM.
• Transmits gear/shift lever position data via CAN communication to the DSC HU/CM. (MTX)
|
|
TCM (ATX)
|
• Transmits gear/selector lever position data via CAN communication to the DSC HU/CM.
|
|
EPS CM
|
• Transmits steering angle data via CAN communication to the DSC HU/CM.
|
|
SAS control module
|
• Detects the lateral-G (vehicle lateral acceleration speed), the yaw rate (vehicle turning angle speed), and the longitudinal-G (vehicle longitudinal acceleration speed) via CAN communication to the DSC HU/CM.
|
|
Brake system warning light
|
• Notifies the driver that the parking brake is applied.
• Notifies the driver of an ABS or EBD malfunction.
|
|
ABS warning light
|
• Notifies the driver of an ABS malfunction.
|
|
TCS/DSC indicator light
|
• Informs the driver that the TCS is operating (drive wheel is spinning).
• Informs the driver that the DSC is operating (vehicle sideslip occurring).
• Informs the driver of DSC system malfunction.
|
|
DSC OFF switch
|
• Transmits driver intention to release TCS/DSC control to the DSC HU/CM.
|
|
DSC OFF indicator light
|
• Informs driver that TCS/DSC control has been released due to DSC OFF switch operation.
|
|
ABS wheel-speed sensor
|
• Detects the rotation condition of each wheel and transmits it to the DSC HU/CM.
|
|
Brake fluid pressure sensor (Built into DSC HU/CM)
|
• Detects the fluid pressure from the master cylinder.
|
|
Brake fluid level sensor (Build into brake fluid reserve tank)
|
• Detects the brake fluid level in the brake fluid reserve tank and transmits it to the DSC HU/CM
|